# 12-15
TODO: 单独重新梳理相关知识点
# 计网
# 1. 常见的HTTP状态码有哪些,分别代表什么意思
同学1的回答
- 常见的HTTP状态码有哪些,分别代表什么意思:
- 200~299:请求成功响应,比如200表示请求成功
- 300~399:请求跳转,比如304表示请求重定向
- 400~499:页面错误,比如404表示页面找不到
- 500~599:服务器错误
同学2的回答
- 200 客户端发送给服务器的请求被正常处理并返回
- 202 接受请求,但是没有处理资源返回
- 204 处理了请求但是没有返回资源
- 301 永久性重定向
- 302 临时性重定向
- 400 表示请求报文中存在语法错误
- 401 未经许可,需要通过HTTP认证
- 403 服务器拒绝该次访问
- 404 表示服务器上无法找到请求的资源
- 405 服务器不允许该类请求
- 500 表示服务器在执行请求时发生了错误
- 502 错误的网关
- 503 服务器不可用
- 504 网关超时
同学3的回答
- 200:一切正常。
- 400:客户端问题
- 500: 服务端问题
- 404:资源不存在
这里在阐述一下几个场景状态码出现的场景:
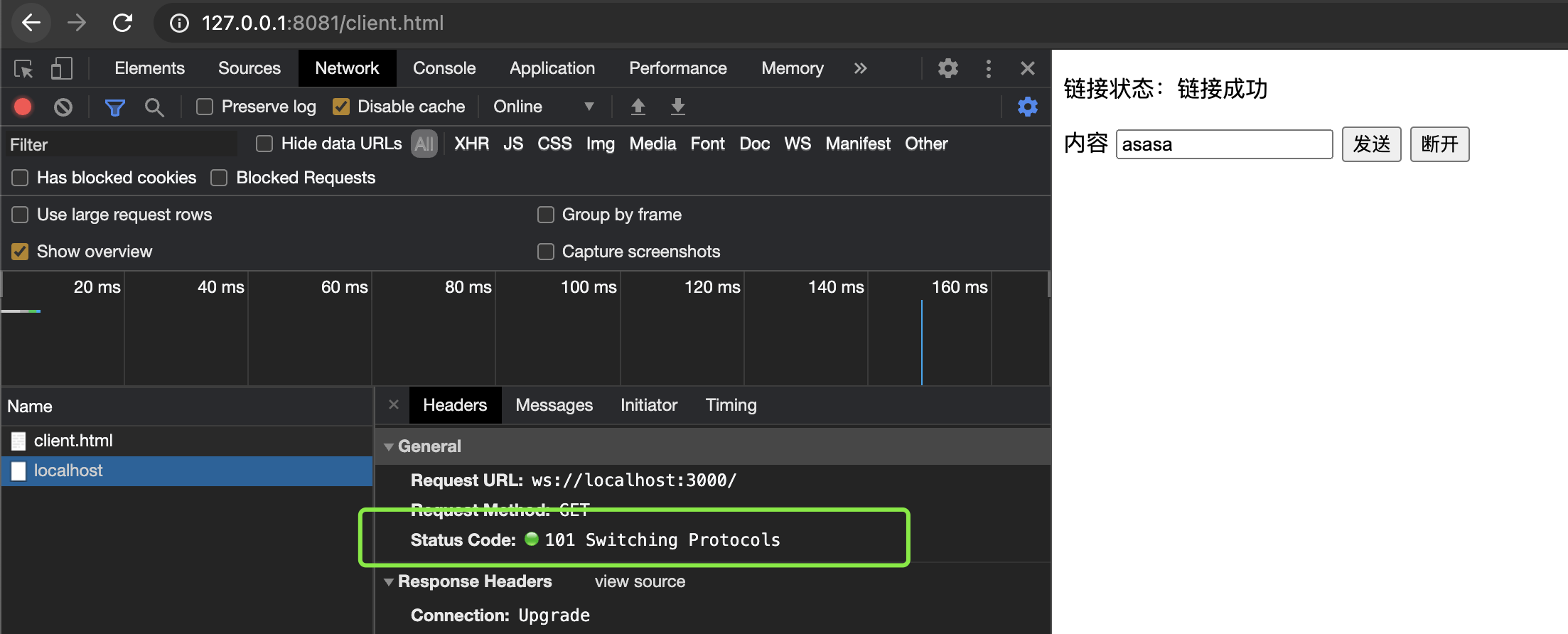
# 101
在HTTP升级为WebSocket的时候,如果服务器同意变更,就会发送状态码 101
查看示例代码
client.html
<body>
<p><span>链接状态:</span><span id="status">断开</span></p>
<label for="content">
内容
<input id="content" type="text">
</label>
<button id="send">发送</button>
<button id="close">断开</button>
<script>
const ws = new WebSocket('ws:localhost:3000', 'echo-protocol')
let status = false
const $status = document.getElementById('status')
const $send = document.getElementById('send')
const $close = document.getElementById('close')
$send.onclick = function () {
const text = document.getElementById('content').value
console.log('发送: ', text);
ws.send(text)
}
ws.onopen = function (e) {
console.log('connection open ...');
ws.send('Hello')
status = true
$status.textContent = '链接成功'
}
$close.onclick = function () {
ws.close()
}
ws.onmessage = function (e) {
console.log('client received: ', e.data);
}
ws.onclose = function () {
console.log('close');
status = false
$status.textContent = '断开连接'
}
ws.onerror = function (e) {
console.error(e);
status = false
$status.textContent = '链接发生错误'
}
</script>
</body>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
server.js
// 需要自行安装 websocket 模块
const WebSocketServer = require('websocket').server;
const http = require('http');
const server = http.createServer(function (request, response) {
console.log((new Date()) + ' Received request for ' + request.url);
response.writeHead(200);
response.end();
});
server.listen(3000, function () {
console.log((new Date()) + ' Server is listening on port 3000');
});
const wsServer = new WebSocketServer({
httpServer: server,
autoAcceptConnections: false
});
function originIsAllowed(origin) {
return true;
}
wsServer.on('request', function (request) {
if (!originIsAllowed(request.origin)) {
request.reject();
console.log((new Date()) + ' Connection from origin ' + request.origin + ' rejected.');
return;
}
var connection = request.accept('echo-protocol', request.origin);
console.log((new Date()) + ' Connection accepted.');
connection.on('message', function (message) {
if (message.type === 'utf8') {
console.log('Received Message: ' + message.utf8Data);
connection.sendUTF(`${new Date().toLocaleString()}:${message.utf8Data}`);
}
});
connection.on('close', function (reasonCode, description) {
console.log((new Date()) + ' Peer ' + connection.remoteAddress + ' disconnected.');
});
});
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
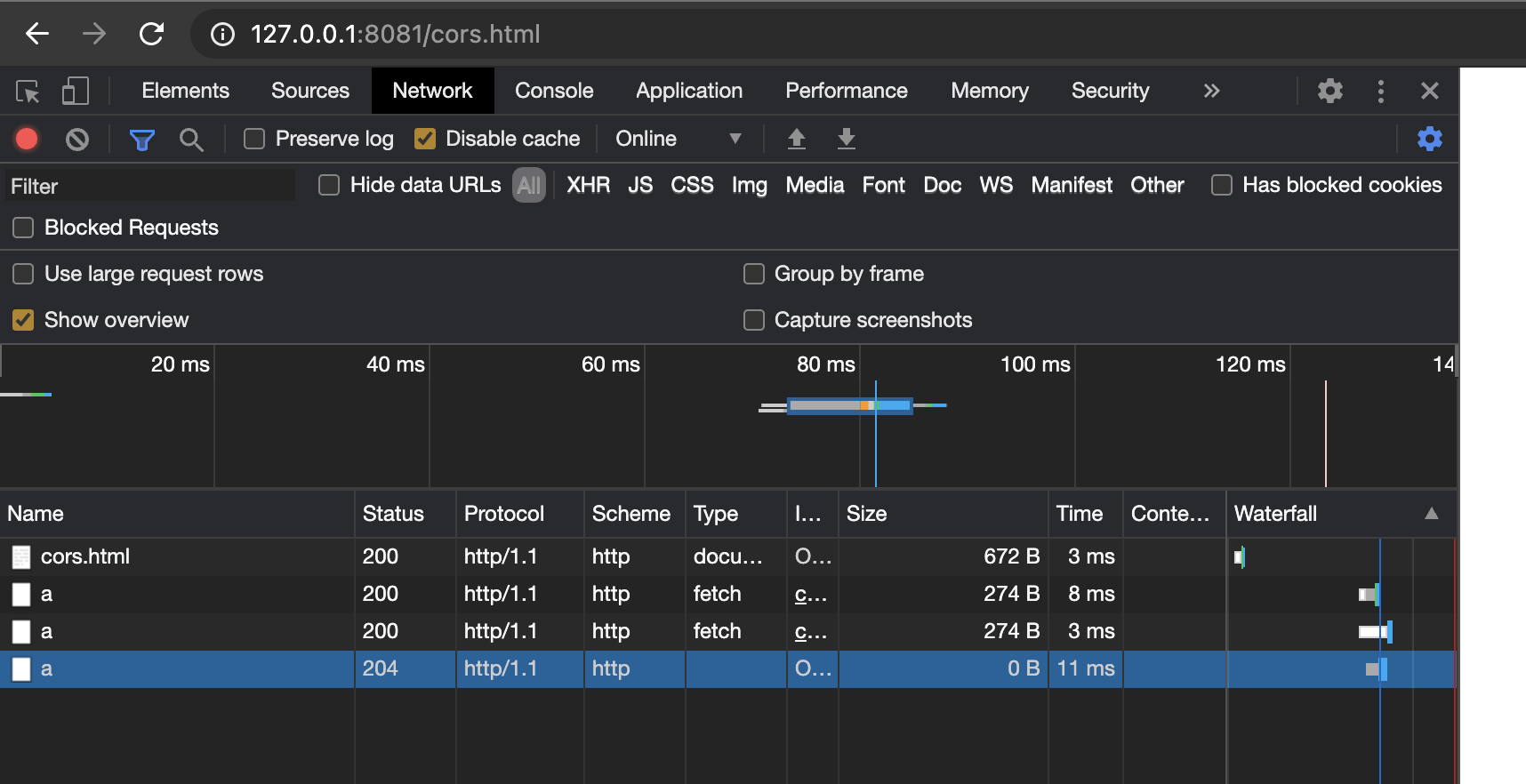
# 204
开启CORS时,当发送复杂请求时,会先发起一个预检请求
如果服务端允许跨域则返回的是204状态码
查看示例代码
cors.html
<body>
<script>
fetch('http://localhost:3000/a',{
method:'get'
})
fetch('http://localhost:3000/a',{
method:'put'
})
</script>
</body>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
cors.js
const http = require('http')
let server = http.createServer(async (req, res) => {
// -------跨域支持-----------
// 放行指定域名
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*')
//跨域允许的header类型
res.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "*")
// 允许跨域携带cookie
res.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Credentials", "true")
// 允许的方法
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Methods', 'PUT, GET, POST, DELETE, OPTIONS')
let { method, url } = req
// 对预检请求放行
if (method === 'OPTIONS') {
res.writeHead(204)
return res.end()
}
console.log(method, url)
res.end('success')
})
// 启动
server.listen(3000, err => {
console.log(`listen 3000 success`);
})
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
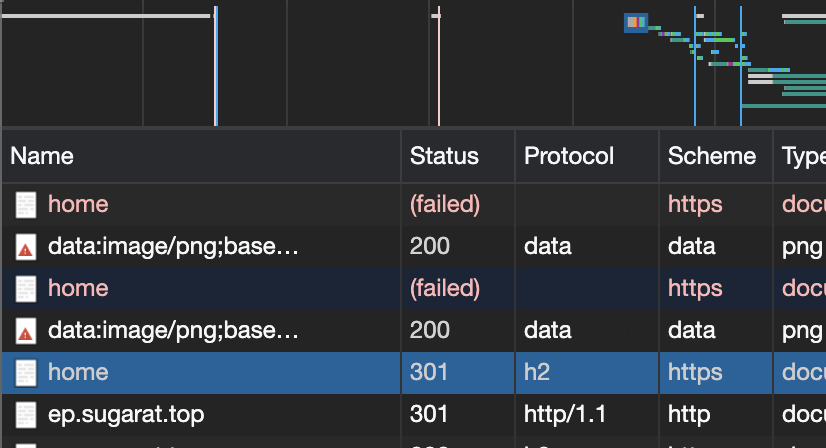
# 301
资源永久重定向
比如访问此链接 (opens new window) 然后观察控制台即可发现 301
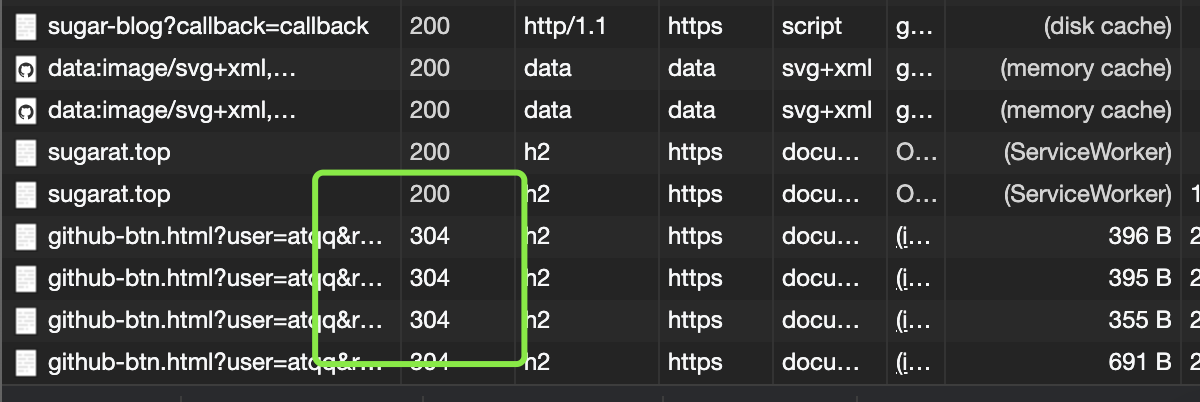
# 304
当客户端拥有可能过期的缓存时,会携带缓存的标识 etag、时间等信息询问服务器缓存是否仍可复用,而304是告诉客户端可以复用缓存
打开当前页面,在控制台中就能发现
# 405
当前的请求方法不被允许
接口允许的方法是post,使用get方法请求 就能获得此状态码
# 415
不支持的媒体类型,检查Content-Type
比如接口使用请求头的媒体类型是 Content-Type:application/json;
你使用 Content-Type:multipart/form-data; 就可能会触发上述错误
# JS
# 1. 如何判断this指向
- 跳转->如何正确判断this?
同学1的回答
- 函数直接执行this指向window
- 函数通过对象调用this指向直接调用的对象
- 通过bind,call,apply调用的函数this指向传入的第一个参数
- 箭头函数内部的this指向外部第一个普通函数的this
- 通过new调用的函数内部this指向新分配的对象
同学2的回答
- 如果是一般函数,this指向全局对象window;
- 在严格模式下"use strict",为undefined.
- 对象的方法里调用,this指向调用该方法的对象.
- 构造函数里的this,指向创建出来的实例
- 箭头函数的this指向指向箭头函数定义时所处的对像
# css
<div class="app">
<div>
<h1>标题</h1>
<p class="color-blue color-red color-yellow">什么颜色</p>
</div>
</div>
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
3
4
5
6
.app p{
color: black;
}
.app .color-yellow{
color: yellow;
}
.app .color-red{
color: red;
}
p.color-color-blue{
color: blue;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 1. 运行后上面的p标签什么颜色
如果无其它未知的全局样式覆盖,那么就是红色
# 2. css样式权重如何计算的
- 跳转->CSS层级关系
同学1的回答
- 内嵌样式权重1000
- id选择器权重0100
- 类选择器权重0010
- 标签选择器权重0001
- 通配符选择器权重0000
- 按选择器包含的种类相加,每位独立不发生进位。结果越大的权重越高
同学2的回答
样式权重
非组合选择器
!important > 行间样式 > id选择器 > 类,伪类和属性选择器 > 类型(标签)选择器和伪元素选择器 > 通配符、子选择器、相邻选择器等的。如*、>、+ > 继承的样式
权重从高到底为 无限大 1000 0100 0010 0001 0000 无 无法进位不行就是不行
10个div也比不上一个.class
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
同学3的回答
内联第一重1000
id第二重100
类第三重10
元素第四重1
然后按照这个顺序计算权重值
值一样的看代码先后
还有一个!important
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 3. 存在冲突时,层叠值(一个元素有多个样式规则)计算规则是怎样的
- 有多个来源(第三方样式,作者样式,作者样式!important),使用高优先级的来源样式
- 是否内联样式,是则使用内联样式
- 权重不同,使用高权重样式
- 权重相同,则使用源码中后声明的样式
同学1的回答
内嵌样式>外部样式=内部样式
后出现的样式>先出现的样式
!important修饰样式的优先级最高
程序员给的样式>继承的样式>浏览器的默认样式
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
同学2的回答
权重高的覆盖权重低的,对于同一权重 讲究先来后到